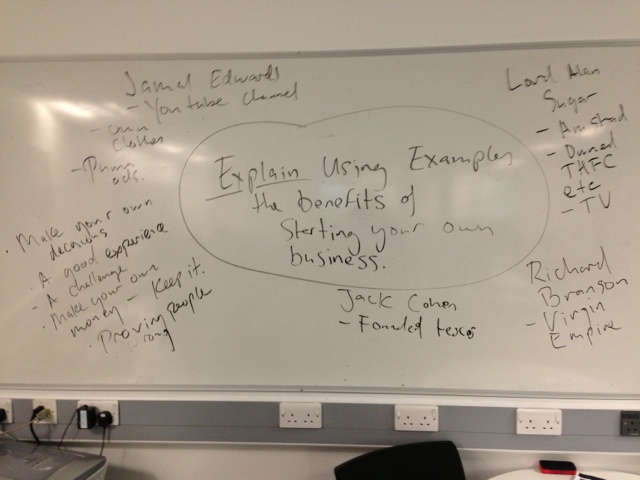
Extension Task 1
Explain using examples the benefits of starting your own business.
You should weigh up pros and cons to get a full and accurate account.
Examples of people who have started their own businesses are; Levi Roots, Bill Gates, Karen Millen and Lord Alan Sugar
To be handed in 26/04/13
Tuesday, 26 March 2013
Monday, 25 March 2013
Project Extension Task 2
Project Extension Task 2
Write about the possible benefits to the business and customer in developing an online business.
You could start with a list of benefits and then expand upon them
These may include financial benefits, time saving benefits etc
Think about the benefits that suit business and customer and the ones that suit them individually too.
To be handed in on 26/04/13
Write about the possible benefits to the business and customer in developing an online business.
You could start with a list of benefits and then expand upon them
These may include financial benefits, time saving benefits etc
Think about the benefits that suit business and customer and the ones that suit them individually too.
To be handed in on 26/04/13
Project extension Task 3
Analyse the different aspects that will affect a business
•To be analysed
•Regulations and laws
•Marketing and sales
•Financial issues
Regulations and laws
•What would the affect be on your online business of the following regulations and laws?
•Minimum wage for employees
•Distance selling act
•Being a partnership
•Being a Ltd Company
•Needing to arrange the payment of your own taxes
Marketing and sales
•What would the affect be on your online business of the following?
•An online marketing campaign
•Full page adverts in a major newspaper
•How could you encourage repeat custom
•What would you do if sales were low
Financial issues
•What would the affect be on your online business of the following financial issues?
•Borrowing money to start your business from friends and family
•Borrowing from the bank
•Costs being greater than profits
•Not maintaining accurate financial records
What to do
•Individually write up or verbally explain your analysis of the three aspects
•ONLY IF YOU HAVE ALREADY SUBMITTED PASSES!
•Regulations and laws
•Marketing and sales
•Financial issues
•This should be approximately 500 words
To be handed in on 26/04/13
•To be analysed
•Regulations and laws
•Marketing and sales
•Financial issues
Regulations and laws
•What would the affect be on your online business of the following regulations and laws?
•Minimum wage for employees
•Distance selling act
•Being a partnership
•Being a Ltd Company
•Needing to arrange the payment of your own taxes
Marketing and sales
•What would the affect be on your online business of the following?
•An online marketing campaign
•Full page adverts in a major newspaper
•How could you encourage repeat custom
•What would you do if sales were low
Financial issues
•What would the affect be on your online business of the following financial issues?
•Borrowing money to start your business from friends and family
•Borrowing from the bank
•Costs being greater than profits
•Not maintaining accurate financial records
What to do
•Individually write up or verbally explain your analysis of the three aspects
•ONLY IF YOU HAVE ALREADY SUBMITTED PASSES!
•Regulations and laws
•Marketing and sales
•Financial issues
•This should be approximately 500 words
To be handed in on 26/04/13
Project Extension Task 5
Project Extension Task 5
Compare the construction features of three different websites (Use the ones from the project or from units 1 or 2)
Please use examples to highlight your points.
Compare
The use of images
The use of video
The use of text
Different ways of navigation
The different purposes of the sites (sell, inform etc)
How these help one of the websites to achieve the aims and objectives of the business
This can be added to existing research if it has not already been done or done from scratch if you feel you have time)
To be handed in on 26/04/13
Compare the construction features of three different websites (Use the ones from the project or from units 1 or 2)
Please use examples to highlight your points.
Compare
The use of images
The use of video
The use of text
Different ways of navigation
The different purposes of the sites (sell, inform etc)
How these help one of the websites to achieve the aims and objectives of the business
This can be added to existing research if it has not already been done or done from scratch if you feel you have time)
To be handed in on 26/04/13
Project Extension Task 6
Project Extension Task 6
Compare the main job roles and functions in two different organisations
Such as Sainsbury’s: retail, administration, finance, IT , HR, logistics and Marketing departments and some of the jobs in them.
With Westminster Kingsway College: Teaching, Marketing, IT, HR and Finance departments and some of the jobs in them.
Discuss how they may be different in organisations with different organisational structures
(Hierarchical, Flat and Matrix)
(You may wish to look over units 1 and 2 for work that can be used as a starting point)
To be handed in on 26/04/13
Compare the main job roles and functions in two different organisations
Such as Sainsbury’s: retail, administration, finance, IT , HR, logistics and Marketing departments and some of the jobs in them.
With Westminster Kingsway College: Teaching, Marketing, IT, HR and Finance departments and some of the jobs in them.
Discuss how they may be different in organisations with different organisational structures
(Hierarchical, Flat and Matrix)
(You may wish to look over units 1 and 2 for work that can be used as a starting point)
To be handed in on 26/04/13
Sunday, 24 March 2013
Task 2b Profit and Loss accounting
You need to show your projected profits and losses in your business plan in the financial section along with your break even and cash flow forecast.
I suggest that you do it for the first year of trading using the figures you have calculated from your expenses and projected sales revenue.
There is a template available from the Microsoft website which is pretty straightforward to use to help you do this.
Any categories that you don't have to use don't.
Any categories that need to be added talk to me and I will tell you where it should go.
It can be downloaded from here

I suggest that you do it for the first year of trading using the figures you have calculated from your expenses and projected sales revenue.
There is a template available from the Microsoft website which is pretty straightforward to use to help you do this.
Any categories that you don't have to use don't.
Any categories that need to be added talk to me and I will tell you where it should go.
It can be downloaded from here
Task 2 D Participate in a Job interview
Task 2 D Participate in a Job interview
You are required to participate in a Job Interview Role Play where you will be the applicant and a tutor will be the interviewer, for either Sales Assistant/Cashier, Administration Assistant or Finance Assistant.
.
Below are a choice of 4 different job descriptions and person specifications on which you will be asked a number of questions.
The questions you will be asked can be accessed below the person specifications. (In a real job interview you would never be given the questions first)
Below are Links to Job Information
Job description/person specification for retail sales assistant here
Sales Assistant interview questions are here
Job description for Sales Assistant here
Person specification for sales assistant here
Sales Assistant interview questions are here
Job description for Administration Assistant here
Person Specification for admin assistant here
Admin assistant questions here
Job description for Finance assistant here
Finance Assistant person spec here
Finance assistant questions here
On Monday 15th of April you will be required to participate in a Job Interview Role Play with either Mark or Genora in room 324 or 325.
The time and place of your role play will be posted on blogger during the Easter Break so you need to check to find out more information!
Sales assistant interview questions
Sales assistant interview questions
You will be asked all of these questions so prepare an answer.
Remember you can use home/work/college experiences as evidence for answering questions.
1. Tell me about yourself?
2. What are your biggest strengths for the role of Retail sales assistant?
3. Why did you leave your last job?
4. What are your career goals starting as a Retail sales assistant?
5. Why do you want to work here?
6. What is your greatest weakness?
7. How many years of experience do you have for this Retail sales assistant position?
8. What motivates you to do your best in the role of Sales assistant?
9. How would you know you were successful on this Sales assistant interview?
10. What do you think are the most important skills in succeeding in sales?
11. Could you sell me this pen?
12. What do co-workers say about you?
13. Are you applying for other jobs?
14. What do you know about our organization?
15. What kind of salary are you looking for?
Finance and Administrative assistant interview questions
Note:You will be asked all of these questions in the interview.
Please have prepared an answer- Remember you do not have to have paid experience you can talk about other areas of your life such as home and college if they are relevant.
1. Tell me about yourself?
2. What are your greatest weaknesses?
3. What experience do you have for Administrative/finance assistant?
4. Why do you think you would do well for Administrative/finance assistant?
5. What kind of salary are you looking for Administrative/finance assistant?
6. Tell me about a time when it was necessary for you to communicate technical information, clearly, to an audience.
7. What plans have you in the near future to take extra technical training, and how will it help your career prospects?
8. Give me an example of an assignment, which you have recently worked on, that involved the learning of a new technical development.
9. How computer literate are you, and which software programs are you familiar with?
10. Have you ever used software to make a work related presentation?
11. Do you know how to use Microsoft Outlook?
12. How fast can you type?
13. What technical skills do you possess?
14. Do you know how to use MS PowerPoint, Word and Excel?
15. What is your typing speed?
Friday, 22 March 2013
Cash flow forecast
Here's a template for cash flow forecast.
Adapt as needed.
https://www.dropbox.com/s/68c5no50icc3enw/cashflow%20model.xls
Adapt as needed.
https://www.dropbox.com/s/68c5no50icc3enw/cashflow%20model.xls
Task 2 c individually create a job description and person specification for a role in your business.
You need to to research job vacancies you should pay attention to the job descriptions, and person specifications As you need to create the following.
1) a job description.
2) a person specification.
3) an advert to go online or in a newspaper.
For a role of your choosing in your business.
In order to do this you will need to create an advert with the job description (eye catching but honest)
A person specification for any applicant to meet - (this is a written set of criteria with skills and abilities that are essential and desirable for a candidate to have)
1) a job description.
2) a person specification.
3) an advert to go online or in a newspaper.
For a role of your choosing in your business.
In order to do this you will need to create an advert with the job description (eye catching but honest)
A person specification for any applicant to meet - (this is a written set of criteria with skills and abilities that are essential and desirable for a candidate to have)
Monday, 18 March 2013
Task 2B sources of advice
You need to think about and discuss the different individuals and organisations that can help you set up a new business.
Some are formal
Some are informal
Individuals
-Solicitors/lawyers
-accountants
-teacher
-mentor
-parents
-friends
Organisations
-Department of Business innovation and Skills
-Bank
-foreign office
-local authority
-C.A.B
- young entrepreneur mentoring orgs.
1)Describe each of these briefly
2)describe which of these you would use and why.
Some are formal
Some are informal
Individuals
-Solicitors/lawyers
-accountants
-teacher
-mentor
-parents
-friends
Organisations
-Department of Business innovation and Skills
-Bank
-foreign office
-local authority
-C.A.B
- young entrepreneur mentoring orgs.
1)Describe each of these briefly
2)describe which of these you would use and why.
Tuesday, 12 March 2013
Task 2b Break even for multiple product businesses
How to Calculate Your Breakeven Point when you sell multiple products/services.
For your business plan you should calculate both how much revenue from sales is required to break even and how many units need to be sold
You need the following information before you can do this:
A) The variable cost price per unit (how much has it cost you to make or buy your product/service)
B) Your selling price per unit (FYI after completing your break-even you may decide to raise or lower your selling price)
C) The number of units you can make or sell in a given period of time such as a year (This will tell you how much you will spend on your stock and how much revenue it will bring in)
D) Your total fixed costs for the same time as C above (you might want to include utilities, wages etc in this to give you a better idea of what your sales need to be to cover all your costs.
This break even formula assumes that the business will sell equal amounts of each product!
If your business has an equal amount of each product please do steps 1,2 and 3 to calculate break-even.
If your business has different levels of each stock item then do steps 1,2,3 and 4 to calculate break-even.
Writing in (italics and brackets is advice or an explanation)
If your business has an equal amount of each product please do steps 1,2 and 3 to calculate break-even.
If your business has different levels of each stock item then do steps 1,2,3 and 4 to calculate break-even.
Writing in (italics and brackets is advice or an explanation)
Scenario: You need to calculate the monthly break-even for a business that sells two products that have a different variable cost price and the same selling price.
- A firm sells two products, chairs and bar stools, for £50 per unit and the variable costs are £25 per unit for chairs and £20 per unit for bar stools.
- The fixed costs for the firm are £20,000 per month.
- If the sales mix is 1:1 (one chair sold for every bar stool sold), what is the breakeven point in pounds of sales and in units of chairs and bar stools?
(As this business has two products that sell equally but have a different cost they will both contribute a different amount to the businesses profits. The % or decimal amount can be calculated as follows it does not matter if you use % or a decimal point in your calculations)
1) You must compute the "weighted average" or gross margin profit percentage for each product, which is calculated as the sum of the gross margin percentage for each product multiplied by its percentage of sales.
- The chair has a gross margin profit percentage of 50 percent or .5 (£50-£25) /.50
- The stool has a gross margin profit percentage of 60 percent or .6: (£50-£20) /.50
- (If there were four products the /.50 would change to /.25. If there were 10 products it would change to /.10 etc)
2) As there are two products being sold Each product accounts for 50 percent of the unit sales of the firm (meaning a 1:1 sales mix).
Therefore, the weighted average gross margin is calculated as follows:
Therefore, the weighted average gross margin is calculated as follows:
- Chair: 50% x 50% = 25%
- Stool: 60% x 50% = 30%
- Weighted average gross margin = 55% (25% + 30%)
Then, you would use the weighted average percentage in the breakeven formula as follows:
breakeven = £20,000 /.55 = £36,363.
3) To calculate the unit sales of each product needed to break-even , take the breakeven sales, multiply by the product's sales mix, and then divide by its price as follows:
breakeven = £20,000 /.55 = £36,363.
3) To calculate the unit sales of each product needed to break-even , take the breakeven sales, multiply by the product's sales mix, and then divide by its price as follows:
- Stools to sell = £36,363 x .50 /£50 = 363 stools
- Chairs to sell = £36,363 x .50/£50 = 363 chairs
(For your business plan you should calculate both how much revenue from sales is required to break even and how many units need to be sold)
4) The break-even point would either be lower or higher depending on which product sold better.
For example If the above Business were to have sales of 70 percent stools and 30 percent chairs, the breakeven point would be reduced to £35,088 because the weighted average gross margin increased to 57 percent.
Conversely, if the business were to sell 30 percent stools and 70 percent chairs, the breakeven point would be increased to £37,736 because the weighted average gross margin decreased to 53 percent.
This is an edited version of an article by Ian Benoliel and the original is available from here. at http://www.entrepreneur.com/article/52102
It is intended to be used as a reference for academic purposes.
Task 2b SWOT template
Please follow the link to find a SWOT template.
It has examples for each criteria on the sides.
Be honest about the business!
https://www.dropbox.com/s/qve1w3sgesq76rn/P1_SWOT_analysis_template.docx
It has examples for each criteria on the sides.
Be honest about the business!
https://www.dropbox.com/s/qve1w3sgesq76rn/P1_SWOT_analysis_template.docx
Task 2 B Business Plan : Break Even Analysis
Business Plan : Break Even Analysis
There are three ways to do this:
1- create a graph as you did in unit 3 p5
2- use the break even formula as you did in unit 3 p4
3- from your cash flow forecast work out when your income meets expenditure.
1- create a graph as you did in unit 3 p5 You need the following equipment to complete this task: A4 graph paper, a ruler, a sharp pencil and an eraser
Important information that you need to calculate to do this
- Fixed costs: These don’t change with use e.g. rent and salary. Add them together, for the sake of your sanity I suggest that you consider utilities and other expenses (not stock) as fixed costs.
- Variable costs (per unit) For a one product business this is simple x the number of units by the price you paid for them. For a multiple product business see here.
- Selling price per unit: One way of doing this is to add 25% to the variable cost price to cover your VC’s
- Maximum sales: The number of items that you have to sell from your VC calculation. This might be based on the maximum you can afford to buy: Such as if you had a budget of £10,000.00 to buy £500.00 items your max sales in a period would be 20.Or it might be based on what you could physically do: Such as if you were a school photographer you would only be able to visit one school a day and be able to visit 5 in a week etc.
What to do
- You need to calculate your maximum revenue based on the figures above and work out a scale for representing this on a graph. (Starting at 0 you should go up in a sensible amount )
- On a piece of graph paper long side horizontally draw a vertical axis. This will represent your costs and income. (Remember to do this based on the calculations above and start at 0)
- Label this axis costs and revenue
- Draw a horizontal axis that will represent your total sales.
- Label this axis units sold.
- Draw a horizontal line at the point where fixed costs occur
- Label this fixed costs.
- Calculate total costs (total fixed costs + total variable costs)
- Using fixed costs as a starting point and ending at the point where maximum sales and revenue can occur draw a line for your total costs
- Calculate your total possible revenue based on total units x selling price
- Mark the point at which maximum units sold and maximum revenue meet.
- Using a pencil and a ruler draw a line from no sales to the mark made previously.
- Label this line total revenue.
- The point at which TC and TR meet is your break-even point.
- Make sure that all lines are labelled.
- Use this formula to check your work:
Break even = total fixed costs
Selling price – variable cost2- use the break even formula as you did in unit 3 p4
You need to calculate the following
- Fixed costs: These don’t change with use e.g. rent and salary. Add them together, for the sake of your sanity I suggest that you consider utilities and other expenses (not stock) as fixed costs.
- Variable costs (per unit) For a one product business this is simple x the number of units by the price you paid for them. For a multiple product business see here.
- Selling price per unit: One way of doing this is to add 25% to the variable cost price to cover your VC’s
- Maximum sales: The number of items that you have to sell from your VC calculation. This might be based on the maximum you can afford to buy: Such as if you had a budget of £10,000.00 to buy £500.00 items your max sales in a period would be 20.Or it might be based on what you could physically do: Such as if you were a school photographer you would only be able to visit one school a day and be able to visit 5 in a week etc.
Then use this formula to work out how many units you will need to sell to break even.
Break even = total fixed costs
Selling price – variable cost
example: TFC = 10,000
SP = 50.00
VC = 20.00
10,000 divided by 50.00 - 20.00 = 180 units
3- from your cash flow forecast work out when your income meets expenditure.
You will need to look at your cash flow forecast and you should be able to see when you will break even. This is less accurate than the first two methods as it is based on what you think will happen rather than what will definitely happen.
Monday, 11 March 2013
Task 2B financial aspects of a business
To be completed in class today 11/03/13
Calculate total start up costs for your business.
You should calculate fixed costs and variable costs separately.
This should include the following:
1) The cost of premises for your business (this can be calculated by researching property prices in the area you are interested in) remember you may have to pay for a year or so in advance and a deposit of 1 months rent. Include business rates if they are applicable.
2) The cost of any equipment you may require ( if you have a shop for example you would need a till, fridges, shelves etc) remembers he little things like stationary any PC's for staff etc.
3) If you are selling goods calculate the cost for your stock or materials that you may require for a month.
4) utilities can be fixed or variable costs and need to be included in your start up costs as best you can.
Calculate total start up costs for your business.
You should calculate fixed costs and variable costs separately.
This should include the following:
1) The cost of premises for your business (this can be calculated by researching property prices in the area you are interested in) remember you may have to pay for a year or so in advance and a deposit of 1 months rent. Include business rates if they are applicable.
2) The cost of any equipment you may require ( if you have a shop for example you would need a till, fridges, shelves etc) remembers he little things like stationary any PC's for staff etc.
3) If you are selling goods calculate the cost for your stock or materials that you may require for a month.
4) utilities can be fixed or variable costs and need to be included in your start up costs as best you can.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)